1. What Is PDT?
Photodynamic therapy is a non-invasive therapy using photosensitizer and laser to effectively destroy cancer cells. PDT was approved by the U.S. FDA for clinical application in 1996 and approved for clinical application by Chinese SFDA in 2003.
Cancer tissue absorbs a great deal of photosensitizer injected intravenously whereas normal tissue absorbs little. Then special laser irradiation is employed to kill tumor. During the process, photosensitizer interacts with cancer cell and leads to intoxication through necrosis of cancer cells on photodynamic effects, thus the tumor gradually disappears.
Surgery →chemotherapy →radiotherapy →immunotherapy →PDT
PDT is considered among top five anti-cancer procedures recognized by international community.
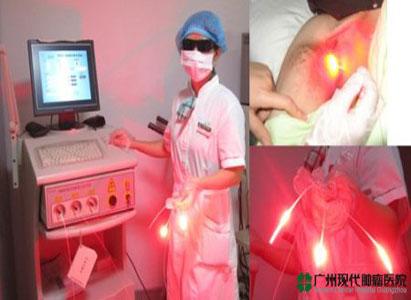
3. Procedures for PDT
First step: photosensitizer is injected. PHOTOFRIN ® is among the most common photosensitizers.
Second step: It usually takes 40 to 50 hours after injection before PDT is performed.
Third step: laser irradiation is applied to focus area to kill cancer cells.
4. Benefits
• Minimally invasive – avoid surgery and wound. Less pain caused.
• Quick effects –the effects show up in 48 to 72 hours
• To prevent cancer recurrence - destroy tiny lesions and minimize tumor recurrence.
• Few complications - low toxicity. It well suits patients with advanced cancer or elderly patients and those with poor physical status.
5. Clinical application
• Oropharyngeal cancer: Effective rate reaches 75% -100% for early oral cancer and nasopharyngeal cancer.
• Esophageal cancer: can remarkably improve obstruction of progressive esophageal cancer; effective in cervical esophageal cancer and disseminated submucosal esophageal cancer; be capable of eliminating intracavity tumor from esophageal cancer treated with stent placement and progressing intracavity.
• Barrett
Barrett’s esophagus: can not only eliminate Barrett’s esophagus epithelium, but also can treat early esophageal adenocarcinoma.
• Lung cancer: cure rate for early bronchial cancer reaches 90%. Improvement rate for progressive obstructive bronchial carcinoma reaches 85%.
• Gastric cancer: cure rate for early gastric cancer is 85%; effective in improving symptoms of progressive gastric cancer
• Bladder Cancer: to treat carcinoma in situ. Effective rate for progressive cancer reaches 71%.
• Other cancers: colorectal cancer, cholangiocarcinoma(especially hilar cholangiocarcinoma), pancreatic, ampullary cancer, abdominal cancer, pleura mesothelioma and abdominal mesothelioma, liver cancer, brain tumor and genitourinary tract cancer.
http://www.asiancancer.com/technology-equipment/118.html

No comments:
Post a Comment